The question of whether a caucus is the same as a primary has puzzled many voters and political enthusiasts alike. As the political landscape continues to evolve, understanding these two fundamental processes is essential for anyone interested in the electoral system in the United States. Both caucuses and primaries play a crucial role in determining party nominees for various elections, but they operate in distinct ways that can significantly impact voter participation and the overall electoral outcome.
In this article, we will delve into the definitions, differences, and implications of caucuses and primaries. We will explore how each system works, their historical context, and how they influence the selection of candidates. By the end of this discussion, you will have a comprehensive understanding of these two electoral processes and their significance in American politics.
So, let’s embark on this informative journey to clarify the distinctions between caucuses and primaries, and why it matters to you as a voter.
Table of Contents
- What is a Caucus?
- What is a Primary?
- Key Differences Between Caucuses and Primaries
- Types of Caucuses
- Types of Primaries
- Historical Context of Caucuses and Primaries
- Impact on Voter Participation
- Conclusion
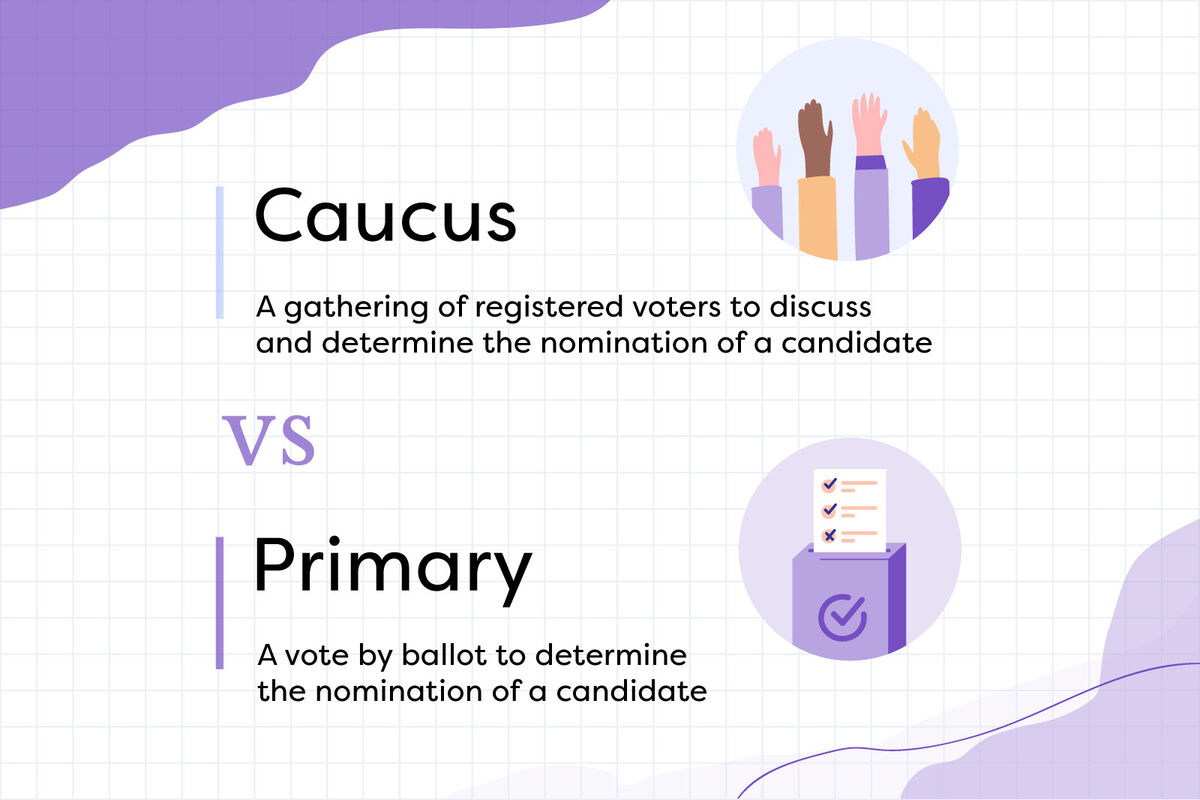
What is a Caucus?
A caucus is a gathering of members of a political party where they discuss and decide on the party's candidate for an upcoming election. Unlike a primary, which is typically a secret ballot, a caucus involves public discussion and often requires participants to physically show their support for a candidate. This process can take several hours and is usually held in local precincts.
Characteristics of a Caucus
- Public Voting: Participants openly express their preferences, making the process more communal.
- Time-Consuming: Caucus events can last several hours due to discussions and deliberations.
- Party Involvement: Typically, caucuses are organized by the political party itself, allowing for internal party dynamics to play a role.
What is a Primary?
A primary is an election in which registered voters from a particular political party vote to choose their party's candidate for the general election. Primaries can be open or closed, depending on the rules set by the state or the political party.
Types of Primaries
- Open Primary: Voters can choose which party's primary to participate in, regardless of their registered party affiliation.
- Closed Primary: Only registered party members can vote in their party's primary, which prevents members of other parties from influencing the selection.
- Semi-Closed Primary: Allows unaffiliated voters to choose which party's primary to vote in, while requiring registered party members to vote in their party's primary.
Key Differences Between Caucuses and Primaries
Understanding the differences between caucuses and primaries is crucial for grasping the electoral process. Here are some of the significant distinctions:
- Voting Method: Caucuses involve public discussion and voting, while primaries utilize a secret ballot.
- Time Commitment: Caucuses require a more substantial time commitment, often several hours, compared to the quicker process of casting a ballot in a primary.
- Voter Participation: Primaries tend to attract more voters due to their simplicity and shorter time requirements.
- Party Control: Caucuses are organized by the political party, which can influence the outcome, while primaries are regulated by state laws.
Types of Caucuses
Caucuses can take various forms, including:
- State Caucuses: Held at the state level to select delegates for national conventions.
- Local Caucuses: Organized within smaller precincts to discuss local issues and select candidates.
- Party Caucuses: Focused on discussing party policies and strategies, in addition to candidate selection.
Types of Primaries
Primaries also come in different formats:
- Presidential Primaries: These determine delegates for national conventions and are pivotal in the selection of presidential candidates.
- State and Local Primaries: Focus on selecting candidates for state and local offices.
- Runoff Primaries: Held when no candidate receives the majority of votes in the initial primary, necessitating a second election.
Historical Context of Caucuses and Primaries
The history of caucuses and primaries dates back to the early days of American politics. Initially, party leaders and elites would select candidates in private meetings. Over time, as democratic ideals spread, the processes evolved to include broader participation from the general public.
The first presidential primary in the United States occurred in 1910 in New Hampshire, setting the stage for the modern primary system. In contrast, caucuses have been used for centuries, with their roots deeply embedded in local political culture.
Impact on Voter Participation
The method of candidate selection—whether through caucuses or primaries—can significantly impact voter engagement. Studies have shown that primaries tend to have higher turnout rates compared to caucuses, primarily due to the accessibility and convenience of the voting process. Factors influencing voter participation include:
- Time of Day: Caucuses often require a significant time commitment, which can deter participation.
- Public Nature: The public aspect of caucuses may discourage some voters from expressing their preferences.
- Awareness and Education: Voters may feel more informed about the primary process, leading to higher engagement.
Conclusion
In summary, while caucuses and primaries both serve the critical function of selecting party nominees, they are fundamentally different in their processes and implications for voter participation. Caucuses involve public discussions and are more time-consuming, whereas primaries offer a more straightforward voting mechanism.
As a voter, understanding these differences is vital for effectively participating in the electoral process. Whether you prefer the engagement of a caucus or the simplicity of a primary, your involvement is crucial in shaping the future of our democracy. We encourage you to share your thoughts in the comments section below, and don't hesitate to explore other articles on our site for more insights into the political landscape.
Thank you for reading, and we hope to see you back here for more informative content on the electoral process and other relevant topics!