As the political landscape evolves, understanding the electoral processes becomes essential for every engaged citizen. The difference between caucus and primary plays a crucial role in how candidates are selected for the presidential race in the United States. Both methods have their unique characteristics and implications for voter participation and candidate selection. In this article, we will delve into the details of these two electoral processes, comparing their structures, functions, and impacts on the democratic system.
In recent years, the importance of knowing the difference between caucus and primary has only grown. With elections often determining the future direction of policies that affect our daily lives, understanding how these processes work can empower voters to make informed choices. Moreover, as different states adopt varying methods, being aware of these differences can help citizens adapt to the electoral landscape.
This article aims to provide an in-depth exploration of the differences between caucus and primary, along with their historical context, advantages, disadvantages, and the implications for voters and candidates alike. By the end of this guide, readers will have a clearer understanding of these electoral processes and how they impact the broader political environment.
Table of Contents
- What is a Caucus?
- What is a Primary?
- Key Differences Between Caucus and Primary
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Caucus and Primary
- Historical Context of Caucus and Primary
- Impact on Voter Participation
- State-Specific Methods of Caucus and Primary
- Conclusion
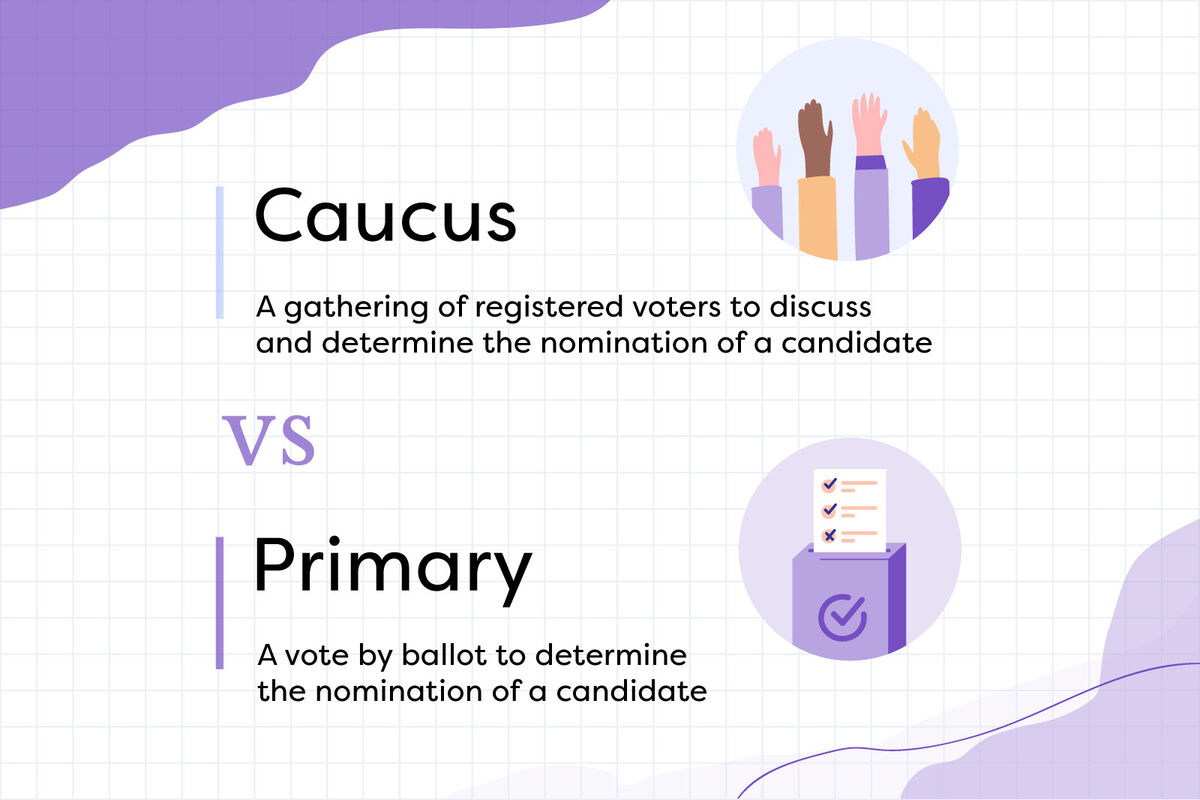
What is a Caucus?
A caucus is a local gathering of party members to discuss and decide on their preferred candidates for an upcoming election. Unlike a primary, where voting is done privately, caucuses often involve open discussions and public voting. Caucuses can vary significantly in format and rules, depending on the state and party.
The Process of a Caucus
- Participants gather at a designated location, often a community center or school.
- Attendees discuss the merits of various candidates.
- After discussions, participants publicly declare their support for a candidate, often through a show of hands or by moving to a designated area.
- Votes are tallied, and delegates are awarded to the candidates based on the results.
What is a Primary?
A primary is a state-level election where party members vote for their preferred candidate to represent the party in the general election. Primaries can be either closed, open, or semi-closed, depending on the state’s regulations regarding who can vote in the primary.
The Process of a Primary
- Voters receive a ballot listing the candidates for their party.
- Voting is conducted privately, similar to a general election.
- The candidate with the most votes secures the party’s nomination.
Key Differences Between Caucus and Primary
Understanding the differences between caucus and primary is essential for grasping the electoral process. Here are the primary distinctions:
- Voting Method: Caucuses involve public discussions and votes, while primaries use private ballots.
- Participation: Caucuses may require more time and commitment, often limiting participation, whereas primaries typically allow for easier access to voting.
- Delegate Allocation: Caucus results may lead to proportional delegate allocation, while primaries can be winner-take-all in some states.
- Timing: Caucuses usually occur earlier in the electoral cycle compared to primaries in many states.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Caucus and Primary
Advantages of Caucus
- Encourages community engagement and discussion among party members.
- Allows for deeper understanding of candidates through direct interaction.
Disadvantages of Caucus
- Often requires a significant time commitment, which can deter participation.
- Public voting may discourage supporters of less popular candidates from participating.
Advantages of Primary
- More accessible due to the private voting process.
- Typically results in higher voter turnout compared to caucuses.
Disadvantages of Primary
- May lead to less engagement and discussion among voters.
- Some states use winner-take-all systems, which can diminish the influence of minority candidates.
Historical Context of Caucus and Primary
The caucus system has its roots in early American politics, where local gatherings were essential for discussing candidates and policies. Over time, the rise of the primary system aimed to increase democratic participation and reduce the influence of party elites. Understanding this historical evolution sheds light on the current electoral landscape.
Impact on Voter Participation
The difference between caucus and primary has significant implications for voter participation. Primaries generally lead to higher turnout rates as they offer a more straightforward voting process. In contrast, the caucus format can limit participation due to its time-intensive nature and public voting methods.
Conclusion
In summary, understanding the difference between caucus and primary is vital for anyone interested in the electoral process. Each method has its unique characteristics, advantages, and disadvantages that affect voter engagement and candidate selection. As elections shape the policies that govern our lives, being informed about these processes empowers voters to make better decisions.
If you found this article helpful, consider leaving a comment or sharing it with others. Stay informed and engaged in the political process!
Thank you for reading, and we hope to see you back for more insightful articles on important topics that matter to you.