The 12th Amendment, ratified in 1804, significantly reformed the process for electing the President and Vice President of the United States. This amendment was introduced to address the complexities and issues that arose from the original electoral process set forth in the Constitution. Over the years, the role of the Vice President has evolved, and understanding this amendment is crucial for comprehending the intricacies of American political structure.
In this article, we will explore the nuances of the 12th Amendment, its historical context, and its implications on the Vice President's role in the electoral process. As we delve deeper into this topic, we will also discuss the importance of the Vice President's position in the modern political landscape and how it has shaped the trajectory of American governance.
Join us as we unpack the layers of the 12th Amendment, examining its significance and the enduring impact it has had on American democracy, particularly concerning the Vice President's responsibilities and authority.
Table of Contents
- Historical Context of the 12th Amendment
- Text of the 12th Amendment
- Implications for the Vice President
- Evolution of the Vice President's Role
- Case Studies of Vice Presidents
- Challenges and Issues Faced
- Current Relevance of the 12th Amendment
- Conclusion
Historical Context of the 12th Amendment
The 12th Amendment was born out of the early challenges faced in the U.S. electoral process. Initially, the Constitution allowed each elector to cast two votes for President, with the candidate receiving the most votes becoming President and the runner-up becoming Vice President. This system led to complications, particularly highlighted during the election of 1800, where Thomas Jefferson and Aaron Burr received the same number of electoral votes, resulting in a protracted political deadlock.
This crisis prompted a call for reform, leading to the proposal and eventual ratification of the 12th Amendment. The amendment established a separate ballot for the President and Vice President, ensuring that electors would explicitly indicate their choices for each position. This change was pivotal in streamlining the electoral process and reducing the likelihood of deadlocks.
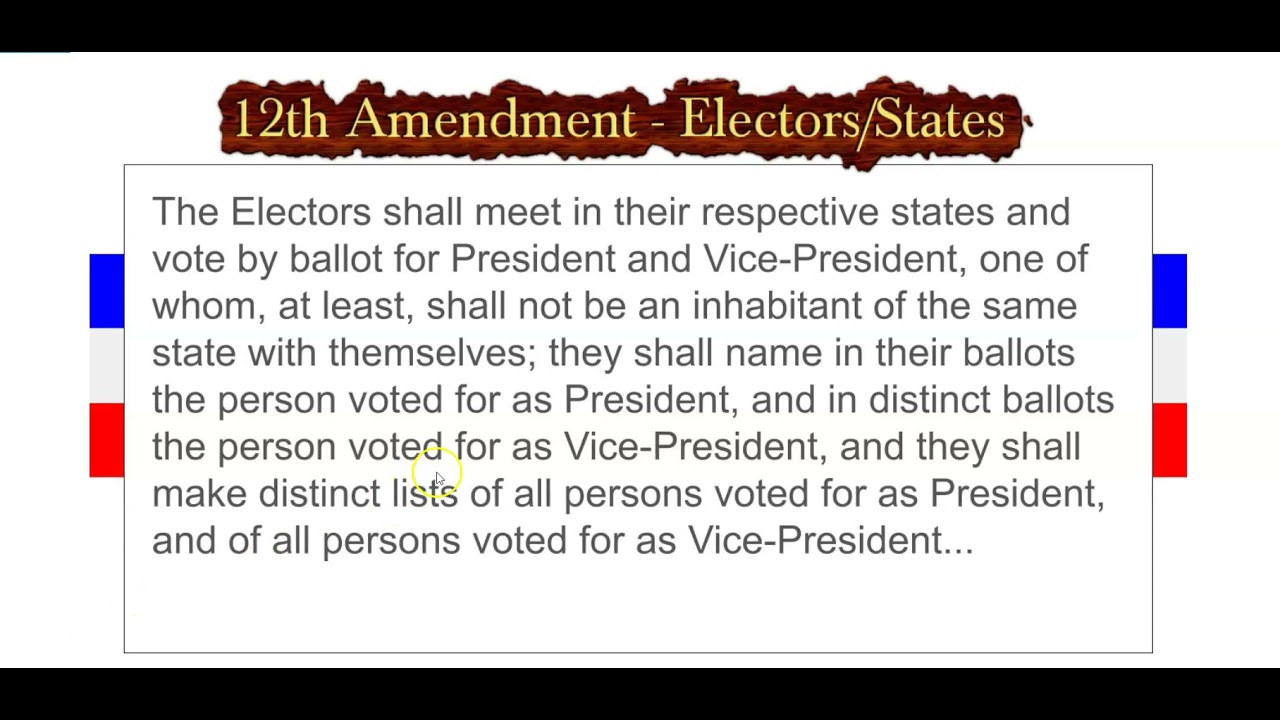
Text of the 12th Amendment
The 12th Amendment states:
“The Electors shall meet in their respective states and vote by ballot for President and Vice President, one of whom, at least, shall not be an inhabitant of the same state with themselves; they shall name in their ballots the person voted for as President, and in distinct ballots the person voted for as Vice President, and they shall make distinct lists of all persons voted for as President, and of all persons voted for as Vice President, and of the number of votes for each, which lists they shall sign and certify, and transmit sealed to the seat of the government of the United States, directed to the President of the Senate; – The President of the Senate shall, in the presence of the Senate and House of Representatives, open all the certificates, and the votes shall then be counted…”
Implications for the Vice President
The 12th Amendment fundamentally altered the Vice President's role in the electoral process. By separating the ballots for President and Vice President, it allowed for the possibility of a President and Vice President from different political parties, which has been a defining characteristic of many modern administrations.
Moreover, the amendment ensured that the Vice President is elected based on the electors' explicit choice, enhancing the legitimacy of the position. This change has had significant implications for political strategy, party dynamics, and governance.
Key Implications Include:
- Reduction of political deadlock in elections.
- Increased political diversity in leadership.
- Enhanced focus on the Vice President's qualifications and role in governance.
Evolution of the Vice President's Role
Since the ratification of the 12th Amendment, the role of the Vice President has seen substantial evolution. Initially viewed as a largely ceremonial position, the responsibilities of the Vice President have expanded significantly over the years.
Modern Vice Presidents often play crucial roles in policy-making, diplomatic relations, and crisis management. This shift reflects the growing complexity of governance and the need for a capable second-in-command.
Factors Contributing to this Evolution:
- The increasing complexity of national and international issues.
- The necessity for effective communication and representation in government.
- The desire for continuity of leadership during crises.
Case Studies of Vice Presidents
Examining specific Vice Presidents provides insight into the practical implications of the 12th Amendment and the evolving role of the Vice President. Notable examples include:
1. Thomas Jefferson and Aaron Burr
The election of 1800, which led to the ratification of the 12th Amendment, is a critical case study. The deadlock between Jefferson and Burr highlighted the need for reform, as both men were from the same party, leading to significant political turmoil.
2. Joe Biden
As Vice President under Barack Obama, Joe Biden's role exemplified the modern Vice President's involvement in key policy discussions and international diplomacy, reinforcing the importance of the Vice Presidential office in contemporary governance.
Challenges and Issues Faced
Despite the significant reforms brought about by the 12th Amendment, challenges remain regarding the Vice President's role and the electoral process in general. Issues such as partisan polarization, election integrity, and the influence of money in politics continue to complicate the electoral landscape.
Moreover, the potential for a President and Vice President from opposing parties raises questions about governance and cooperation within the executive branch.
Current Relevance of the 12th Amendment
In today's political climate, the relevance of the 12th Amendment is more pronounced than ever. With increasing political polarization and the emergence of third-party candidates, the electoral process continues to evolve. Understanding the implications of the 12th Amendment is essential for comprehending these dynamics and their impact on American democracy.
Conclusion
In summary, the 12th Amendment has played a pivotal role in shaping the electoral process for the President and Vice President of the United States. By establishing separate ballots, it has reduced the potential for electoral deadlock and enhanced the legitimacy of the Vice President's role. As we move forward in an increasingly complex political landscape, understanding the implications of this amendment remains crucial for both citizens and political leaders.
We invite you to share your thoughts on the 12th Amendment and its impact on the Vice President's role in the comments below. Your insights can contribute to a broader understanding of this vital aspect of American governance.
Thank you for reading, and we hope you found this article informative. Please feel free to explore more of our content on U.S. history and governance.